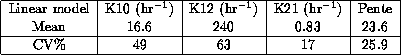Next: 8
Population Distribution of
Up: PAGE '95: ABSTRACT LIST
Previous: 6
Population of Vancomycine
D. Breilh(1) ,
C. Pobel(1) ,
C. Roth(2) , M.C. Saux(1) , G.Janvier(2)
Laboratory of Clinical Pharmacokinetic, Bordeaux II University, France(1)
Anaesthesiology ward, Haut-Leveque hospital, Bordeaux II University, France(2)
10 patients were investigated. Their average characteristics are:
age 65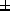 8.7 years, weight 75.7
8.7 years, weight 75.7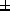 9.9 kg. They were given an
average total dose of 409
9.9 kg. They were given an
average total dose of 409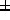 69.67 mg/kg of sufentanyl during
anaesthesia: 6 mg/kg from induction to sternotomy (one or several
bolus), and 1 mg/kg in continue with an electric seringe to
increase the duration of anaesthesia. Blood samples mean is
18
69.67 mg/kg of sufentanyl during
anaesthesia: 6 mg/kg from induction to sternotomy (one or several
bolus), and 1 mg/kg in continue with an electric seringe to
increase the duration of anaesthesia. Blood samples mean is
18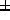 2.7 per patient (extreme: 15-23) and blood sampling was
done between 0 and 18 hours after anaesthesia was induced and
depends on the duration of the operation.
2.7 per patient (extreme: 15-23) and blood sampling was
done between 0 and 18 hours after anaesthesia was induced and
depends on the duration of the operation.
Pharmacological effects studied are haemodynamic as the mean
arterial blood pressure (MAP) was taken in each patient when blood
samples were taken. The PK/PD model is a two-compartment
pharmacokinetic model, whose central compartment is linked to the
effect compartment. The sigmoid Emax model (Hill's equation) as
well as a linear model have been used for studying the
relationship between the effect (E%) and the concentration in the
effect compartment. Results (on model plasma concentration):

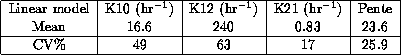
The values of parameters (K10, K12, K21) are similar between the
Emax model and the linear model. The biophase can be put on the
central level with these results. This is interesting as far as
the MAP is a very easy parameter to follow in anaesthesia and is
a means of controlling the quality of anaesthesia.
harnisch@pollux.zedat.fu-berlin.de
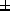 8.7 years, weight 75.7
8.7 years, weight 75.7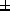 9.9 kg. They were given an
average total dose of 409
9.9 kg. They were given an
average total dose of 409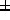 69.67 mg/kg of sufentanyl during
anaesthesia: 6 mg/kg from induction to sternotomy (one or several
bolus), and 1 mg/kg in continue with an electric seringe to
increase the duration of anaesthesia. Blood samples mean is
18
69.67 mg/kg of sufentanyl during
anaesthesia: 6 mg/kg from induction to sternotomy (one or several
bolus), and 1 mg/kg in continue with an electric seringe to
increase the duration of anaesthesia. Blood samples mean is
18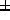 2.7 per patient (extreme: 15-23) and blood sampling was
done between 0 and 18 hours after anaesthesia was induced and
depends on the duration of the operation.
2.7 per patient (extreme: 15-23) and blood sampling was
done between 0 and 18 hours after anaesthesia was induced and
depends on the duration of the operation.