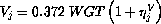
M.T. Mateu-Garcia, J.J. Perez-Ruixo, V.G. Casabo-Alos, N.V. Jimenez-Torres
Pharmacy Service, Hospital Dr. Peset, Department of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutics, University of Valencia, Valencia, Spain
INTRODUCTION
Today, gentamicin (GENT) is still used in serious infections in the critical ill patients. To produce efficacious and safe dosage regimens, variability in the population pharmacokinetic parameters (PPK) must be explained and quantified through the identification of covariates. The optimal situation is to define a priori dosage regimen based on the covariate measurements to finally optimize the individual treatment including the patients drug serum concentrations.
OBJECTIVE
To identify relationships between PPK parameters of gentamicin and APACHE II and other covariates.
METHOD
23 adult ICU patients, with unstable renal function, were given standard doses of gentamicin 30 min IV infusion. 123 serum concentrations (Cp) were collected 30 min after the end of infusion (peak) and just before the dose (trough) (5.4 Cp/patient).
A one compartment model was used in model development (NONMEM) to fit the Cp-time values. Estimates for clearance (Cl) and distribution volume (Vd) were sought.
The covariate data collected on each patient included weight (WGT), length of therapy(TTO), serum creatinine (Cr), Apache II score, white blood count (LEUC), blood urea nitrogen (UREA), corporal temperature (TEMP) and body surface area (BSA).
Covariates collected were forward incorporated one by one in the population model since a full model was built. The p value required to include a new covariate into the model was <0.01. A more conservative p value of <0.005 was required to conserve the covariate in the final model (backward process).
RESULTS
GENT Vd (L) was directly related with weight (Kg). GENT Cl (L/h) was related with creatinine clearance (CLCr), weight, and Apache II score at first (APA1) and last (APA2) day of therapy.
Proportional interindividual variability model was applied to best describe the PPK parameters. The random error added to the serum concentrations was a combination of an additive and a constant coefficient of variation model.
The regression relationships adopted in the final model were as follows:
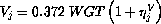
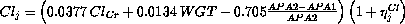
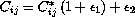
Values of interindividual and intraindividual variances estimates and minimum objective function achieved were:
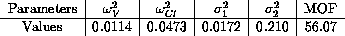
CONCLUSION
Apache II score appears as a good covariate to establish the PPK parameter in critical ill patients.